In this tutorial we are going to be looking at the SGDR or as referred to in the timm library - the cosine scheduler in little more detail with all the supporting hyperparams.
The SGDR schedule as mentioned in the paper looks like:
from timm.scheduler.cosine_lr import CosineLRScheduler
from nbdev.showdoc import show_doc
The CosineLRScheduler as shown above accepts an optimizer and also some hyperparams which we will look into in detail below. We will first see how we can train models using the cosine LR scheduler by first using timm training docs and then look at how we can use this scheduler as standalone scheduler for our custom training scripts.
To train models using the cosine scheduler we simply update the training script args passed by passing in --sched cosine parameter alongside the necessary hyperparams. In this section we will also look at how each of the hyperparams update the cosine scheduler.
SGDR but in timm this is referred to as cosine scheduler. They are both one and the same with minor implementation difference. The training command to use cosine scheduler looks something like:
python train.py ../imagenette2-320/ --sched cosine
This way we start to use the cosine scheduler with all the defaults. Let's now look at the associated hyperparams and how that updates the annealing schedule.
This is the optimizer that will be used for the training process.
from timm import create_model
from timm.optim import create_optimizer
from types import SimpleNamespace
model = create_model('resnet34')
args = SimpleNamespace()
args.weight_decay = 0
args.lr = 1e-4
args.opt = 'adam'
args.momentum = 0.9
optimizer = create_optimizer(args, model)
This optimizer object created using create_optimizer is what get's passed to the optimizer argument.
The initial number of epochs. Example, 50, 100 etc.
Defaults to 1.0. Updates the SGDR schedule annealing.
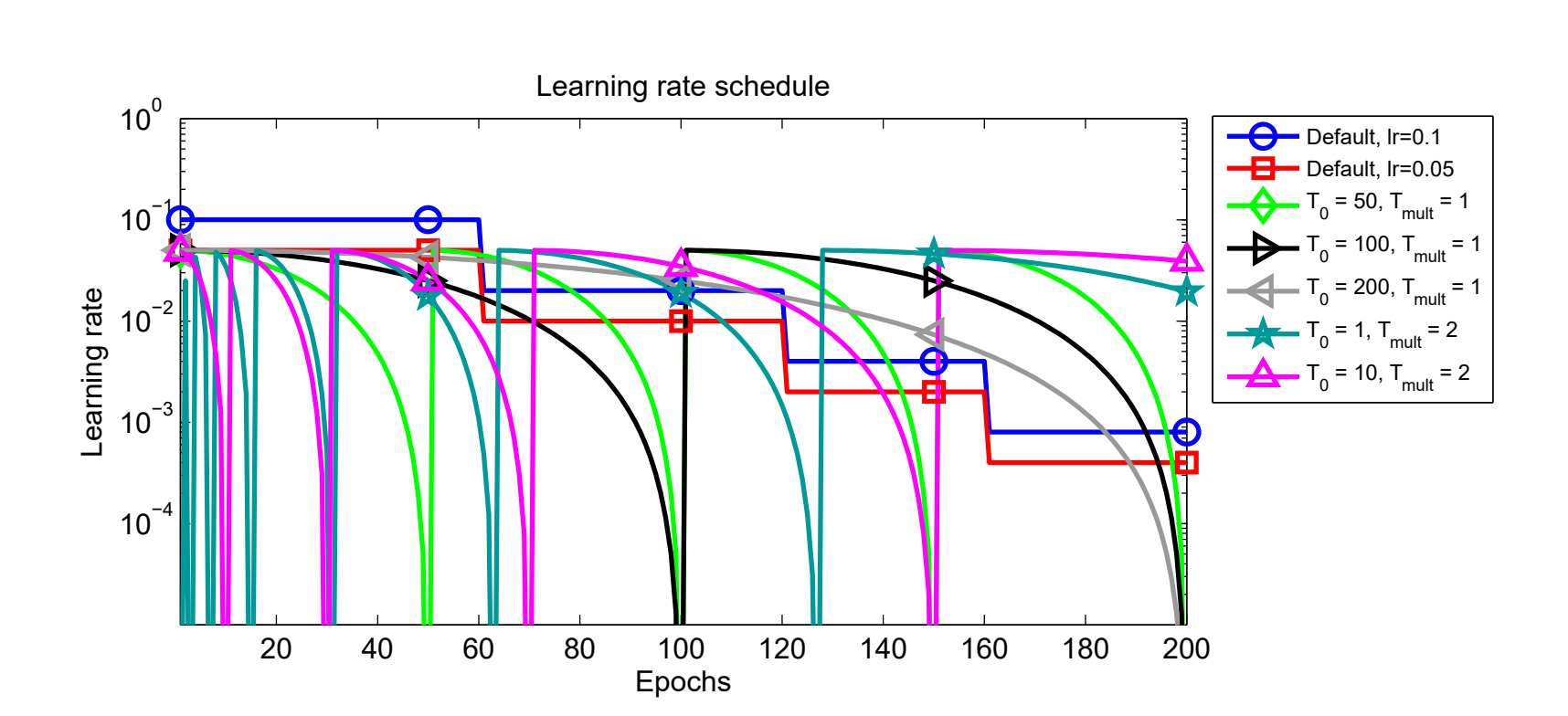
As shown in the image below, here T0 is the t_initial hyperparameter and Tmult is the t_mul hyperparameter. One can see how updating these parameters updates the scheduler.
Defaults to 1e-5. The minimum learning rate to use during the scheduling. The learning rate does not ever go below this value.
When decay_rate > 0 and <1., at every restart the learning rate is decayed by new learning rate which equals lr * decay_rate. So if decay_rate=0.5, then in that case, the new learning rate becomes half the initial lr.
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def get_lr_per_epoch(scheduler, num_epoch):
lr_per_epoch = []
for epoch in range(num_epoch):
lr_per_epoch.append(scheduler.get_epoch_values(epoch))
return lr_per_epoch
num_epoch = 50
scheduler = CosineLRScheduler(optimizer, t_initial=num_epoch, decay_rate=1., lr_min=1e-5)
lr_per_epoch = get_lr_per_epoch(scheduler, num_epoch*2)
plt.plot([i for i in range(num_epoch*2)], lr_per_epoch);
num_epoch = 50
scheduler = CosineLRScheduler(optimizer, t_initial=num_epoch, decay_rate=0.5, lr_min=1e-5)
lr_per_epoch = get_lr_per_epoch(scheduler, num_epoch*2)
plt.plot([i for i in range(num_epoch*2)], lr_per_epoch);
Defines the number of warmup epochs.
The initial learning rate during warmup.
num_epoch = 50
scheduler = CosineLRScheduler(optimizer, t_initial=num_epoch, warmup_t=5, warmup_lr_init=1e-5)
lr_per_epoch = get_lr_per_epoch(scheduler, num_epoch)
plt.plot([i for i in range(num_epoch)], lr_per_epoch, label="With warmup");
num_epoch = 50
scheduler = CosineLRScheduler(optimizer, t_initial=num_epoch)
lr_per_epoch = get_lr_per_epoch(scheduler, num_epoch)
plt.plot([i for i in range(num_epoch)], lr_per_epoch, label="Without warmup", alpha=0.8);
plt.legend();
As we can see by setting up warmup_t and warmup_lr_init, the cosine scheduler first starts with a value of warmup_lr_init, then gradually progresses up to the initial_lr set in the optimizer which is 1e-4. It takes warmup_t number of epochs to go from warmup_lr_init to initial_lr.
Defaults to False. If set to True, then every new epoch number equals epoch = epoch - warmup_t.
num_epoch = 50
scheduler = CosineLRScheduler(optimizer, t_initial=num_epoch, warmup_t=5, warmup_lr_init=1e-5)
lr_per_epoch = get_lr_per_epoch(scheduler, num_epoch)
plt.plot([i for i in range(num_epoch)], lr_per_epoch, label="Without warmup_prefix");
num_epoch = 50
scheduler = CosineLRScheduler(optimizer, t_initial=num_epoch, warmup_t=5, warmup_lr_init=1e-5, warmup_prefix=True)
lr_per_epoch = get_lr_per_epoch(scheduler, num_epoch)
plt.plot([i for i in range(num_epoch)], lr_per_epoch, label="With warmup_prefix");
plt.legend();
In the example above we can see how the warmup_prefix updates the LR annealing schedule.
The number of maximum restarts in SGDR.
num_epoch = 50
scheduler = CosineLRScheduler(optimizer, t_initial=num_epoch, cycle_limit=1)
lr_per_epoch = get_lr_per_epoch(scheduler, num_epoch*2)
plt.plot([i for i in range(num_epoch*2)], lr_per_epoch);
num_epoch = 50
scheduler = CosineLRScheduler(optimizer, t_initial=num_epoch, cycle_limit=2)
lr_per_epoch = get_lr_per_epoch(scheduler, num_epoch*2)
plt.plot([i for i in range(num_epoch*2)], lr_per_epoch);
If set to False, the learning rates returned for epoch t are None.
num_epoch = 50
scheduler = CosineLRScheduler(optimizer, t_initial=num_epoch, t_in_epochs=False)
lr_per_epoch = get_lr_per_epoch(scheduler, num_epoch)
lr_per_epoch[:5]
Add noise to learning rate scheduler.
The amount of noise to be added. Defaults to 0.67.
Noise standard deviation. Defaults to 1.0.
Noise seed to use. Defaults to 42.
If set to True, then, the an attributes initial_lr is set to each param group. Defaults to True.